BNG (Broadband Network Gateway)
Over recent years, ‘cloud-native’ service providers have developed ways to build and run massive data centers with a high degree of automation, to reduce operational overheads and deliver levels of service agility beyond traditional carrier infrastructure. RtBrick’s open BNG brings these same benefits to carrier access networks, by disaggregating software from hardware and applying the same battle-hardened DevOps cloud automation tools that have been adopted by the world’s biggest cloud providers.
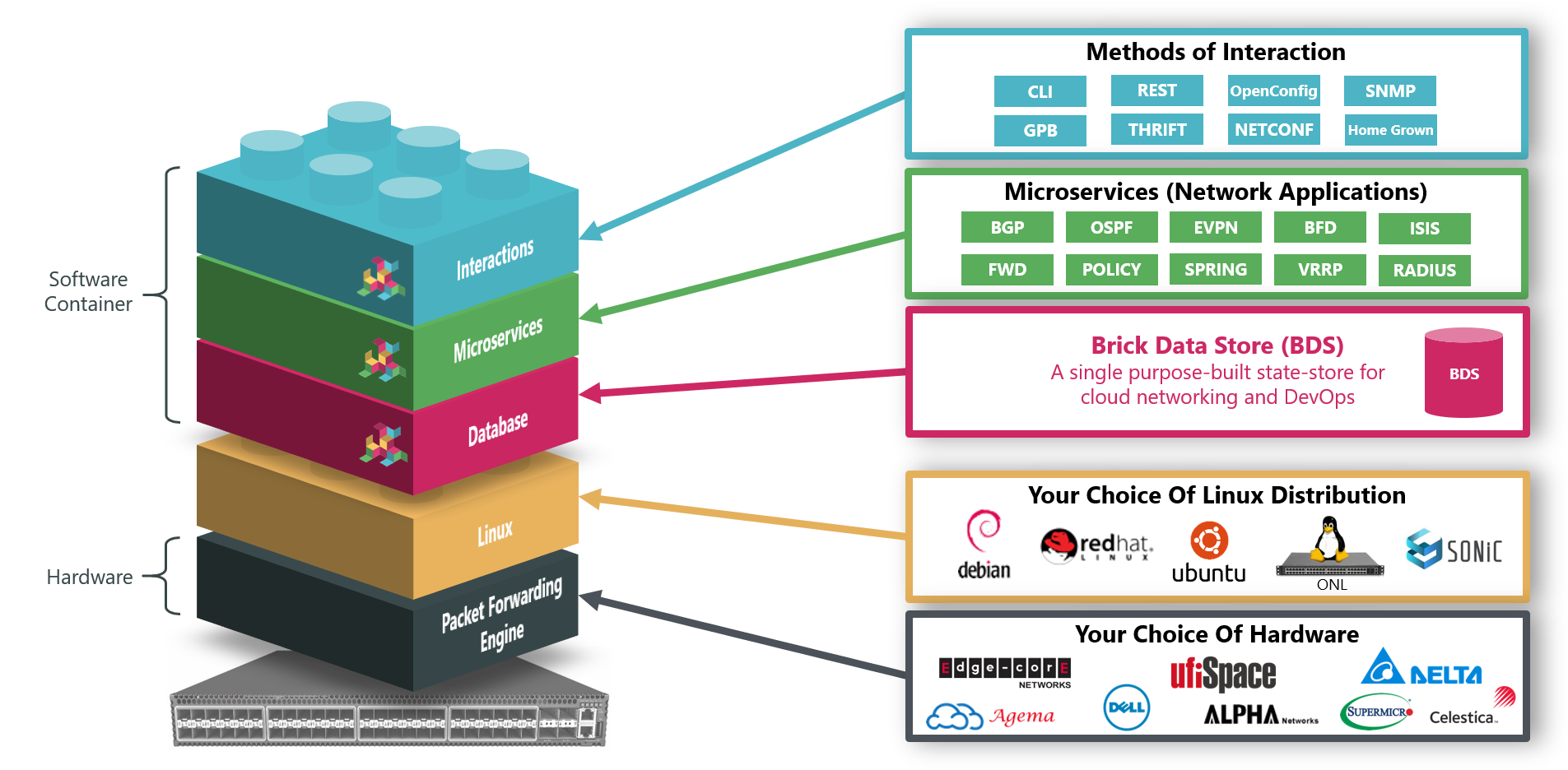
The RtBrick BNG is delivered as a software container, running on the Open Network Linux (ONL) provided by the hardware SKU manufacturers, which handles peripherals such as LEDs, temperature sensors, and so on. There are no dependencies on either the kernel or the hardware platform components, so RtBrick’s containers can be run on the Linux version of your choice.
The RtBrick BNG software runs on low-cost but powerful bare-metal switches as an open BNG. It is hugely scalable using a Spine-Leaf architecture.
Benefits
RtBrick’s open BNG software delivers some significant benefits compared to traditional monolithic systems:
· Greater agility – you can add new services in weeks rather than years
· Reduced risk – no more vendor lock-in and a simpler automated operating environment based on Linux OS
· Cloud cost-levels – leverage low-cost merchant silicon and automate your operations like a ‘cloud-native’ with Zero-Touch Provisioning
· Massive scalability - supporting hundreds of thousands of subscribers on a single BNG, with sub-second convergence of the full Internet routing table
Agility
ZTP (Zero-Touch-Provisioning) ensures that each switch is booted, provisioned and operational without requiring manual intervention. This means that you can add capacity, or roll-out new service features, in a matter of minutes instead of days or weeks. The software itself is developed using Agile methodologies so that features are rapidly prototyped and implemented, reducing the time-to-market for new services.
Reduced risk
RtBrick’s BNG software is compiled for your specific use-case, using only the features you need. With an order of magnitude fewer lines of code, and a single state database rather than hundreds, the whole system is less complex, less prone to bugs and has much faster restart times. It also allows you to pick and mix between the latest silicon and the best available software.
Cloud cost-levels
Now you can take advantage of the low cost-points of merchant silicon on your choice of bare-metal switches, significantly reducing your capex bill. And opex costs can be reduced by automating your operations, using ZTP and the same Web2.0 operational tools that the ‘cloud-natives’ use to run their infrastructure.
Deployment at Smaller Scale
For small to medium deployments, all BNG functionality can be operated on a single low-cost open switch as a Consolidated BNG. A Consolidated BNG includes both the customer-facing BNG functions, to terminate subscriber services, and the core-facing routing functions, in the same platform. A Consolidated BNG is very economical where there are lower concentrations of subscribers. It can also run on smaller form-factor hardware, that is hardened for deployments in cabinets and cell-sites.
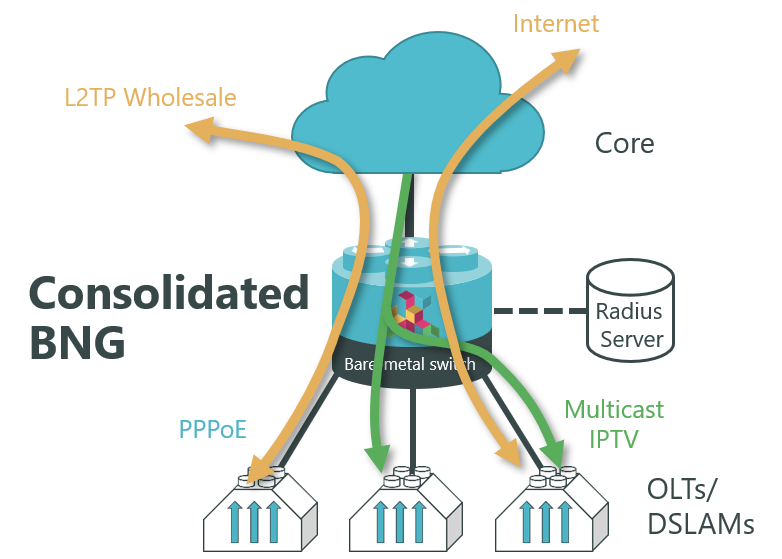
Consolidated BNG on a single switch
The ability to highly distribute the BNG deeper into the network also enables services to be terminated closer to compute and storage that is located closer to consumers.
Deployment at High Scale
The BNG’s subscriber management capacity can also be provided in a scale-out architecture called the Point-Of-Deployment (PoD), also known as a SEBA PoD (SDN Enabled PoD). A large-scale PoD consists of Access Leaf Routers aggregated by a layer of Spine Leaf Routers in an auto-provisioned CLOS topology. The Access Leaves deliver subscriber management functionality. For even greater scalability a layer of Border Leaves can be added to provide more connectivity to the core of the provider network.
 Disaggregated BNG and service cross connect
Disaggregated BNG and service cross connect
The leaves can be scaled out horizontally to increase the number of subscribers supported on the PoD, providing a pay-as-you-grow architecture. PPPoE Subscribers can be terminated on the Access Leaf Routers or tunneled to an LNS over L2TPv2. L2 Cross Connect (L2X) allows subscriber traffic to be tunnelled out of the PoD at Layer 2, providing wholesale connectivity.
Legacy Services
Our Open BNG software can deliver most of your complex broadband services, with HQoS schemes and IPTV support, for example. But you can also re-use your existing infrastructure to continue to provide lower volume legacy services, and optimize the rest of the network for the bulk of your traffic - providing large volumes of high bandwidth services at a lower cost-point with a web-scale operating environment. So your RtBrick BNG can act as a service cross-connect, routing each subscriber to the appropriate network infrastructure and extending the life of your high-cost legacy BRAS or BNG systems, for example.
Management and Operations
Along with a traditional CLI, more ‘cloud-native’ means of interactions are also supported, such as RESTCONF. RtBrick’s Management System, RBMS, takes this a step further, by providing network level workflows such as Image Lifecycle Management, Network Upgrades and Event and Log Management. RBMS actions are available through REST APIs making them easy to integrate into existing OSS systems. RBMS provides a single point of interaction for operations staff – from provisioning and management to monitoring and debugging.
The result is a BNG that can be managed using the latest Web2.0 tools through a ‘single pane of glass’, with Zero-Touch-Provisioning.
Watch a demo of RtBrick open BNG software
Features
The features supported by RtBrick FullStack are expanding all the time, because it's much faster for us to add and test new features than it is using a traditional monolithic code base. Currently supported features include:
| Features * | BNG |
| General | |
| Routing Policy | ✔ |
| LDP | ✔ |
| L2X | ✔ |
| BGP | |
| IPv4 | ✔ |
| IPv6 | ✔ |
| LU-v4 | ✔ |
| LU-v6 | ✔ |
| VPNv4 | ✔ |
| VPNv6 | ✔ |
| Add-path | ✔ |
| Multi-path | ✔ |
| Multi-hop | ✔ |
| Segment Routing | ✔ |
| 4-Byte AS | ✔ |
| TCP-AO | ✔ |
| ISIS | |
| IPv4 | ✔ |
| IPv6 | ✔ |
| Segment Routing | ✔ |
| OSPF | |
| IPv4 | ✔ |
| IPv6 | |
| Segment Routing | ✔ |
| Forwarding Plane | |
| VPP | ✔ |
| ACLs - IPv4/v6, L2 | ✔ |
| QoS/HQoS (policing, scheduling, queuing, hierarchical) | ✔ |
| Access | |
| Radius support | ✔ |
| PPPoE - IPv4/v6 | ✔ |
| L2TPv2 (LAC) - IPv4/v6 | ✔ |
| Accounting (Time/Volume based) | ✔ |
| IPTV | |
| Multicast - PIM, MVPN, IGMP v2/3 (all partial RFC compliance) | ✔ |
| Multicast - SSM Mapping | ✔ |
| Radius integration for subscriber channel policy, blacklisting and whitelisting | ✔ |
| Sub-second channel zap time | ✔ |
| Preview up to 15 other channels | ✔ |
| IGMPv2 for older set-top box support | ✔ |
| IPTV usage statistics | ✔ |
| Operations | |
| Lawful Intercept (including multicast) | ✔ |
| ResmondD (RtBrick resource monitoring application) | ✔ |
| CLI | ✔ |
| Inband Management | ✔ |
| ZTP Provisioning | ✔ |
| RBMS (RtBrick Management System) | |
| Rules Engine | ✔ |
| Topology Discovery & Inventory | ✔ |
| REST API | ✔ |
| Microservice | ✔ |
| Dynamic Service Selection | ✔ |
* may include some road-map features
Example: Deutsche Telekom's next generation access project
Deutsche Telekom is a good example of a carrier looking to benefit from a disaggregated access network, with their Access 4.0 project.
“The focus is on having a more open, more flexible solution. The whole story is about disaggregation of hardware and software. RtBrick brings a piece of software that sits on the switches. They have built software that can program Broadcom chips, so they do the full BNG function.” Robert Soukup, DT’s senior program manager for Access 4.0 (quoted in an interview with FierceTelecom, March 2019)
Compatible Hardware
RtBrick's Full Stack routing software can operate on many bare metal switches, depending on your performance and port count requirements. You can find details of compatible hardware here.

